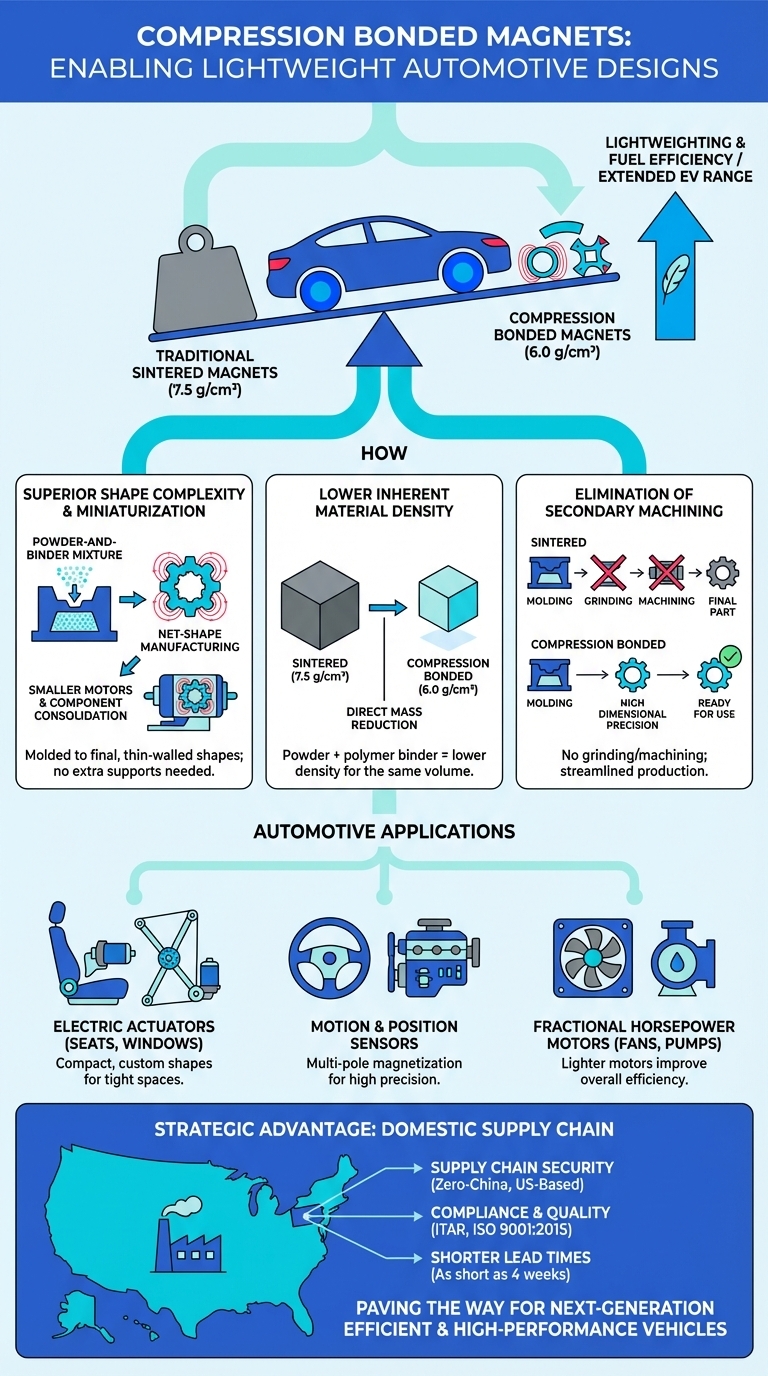
Compression bonded magnets enable lightweight automotive designs by allowing for complex, thin-walled shapes that require less material. Their unique manufacturing process forms magnets to their final net shape, eliminating the need for heavy, bulky components and allowing seamless integration into compact systems without sacrificing performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do compression bonded magnets help make cars lighter?
Compression bonded magnets contribute to lightweighting in three key ways: 1) They can be molded into complex, thin-walled net shapes that require less material and eliminate bulky support structures. 2) They have a lower inherent material density (approx. 6.0 g/cm³) compared to denser sintered magnets (approx. 7.5 g/cm³). 3) Their net-shape manufacturing process eliminates the need for heavy secondary machining.
What are the main differences between compression bonded and sintered magnets?
The primary difference is in the manufacturing process and material composition. Compression bonded magnets are made from magnetic powder mixed with a polymer binder, which is then pressed into a final, complex shape. This allows for superior design flexibility and lower density. Sintered magnets are denser, more brittle, and often require extensive grinding and machining to achieve their final dimensions, which limits their shape complexity.
What are some common automotive applications for compression bonded magnets?
They are ideal for automotive components where reducing weight and size is critical. Common applications include electric actuators for power seats, windows, and sunroofs; high-precision motion and position sensors for engine timing and stability control; and fractional horsepower motors for cooling fans, fluid pumps, and HVAC blowers.
Is there a domestic US supply chain for compression bonded magnets?
Yes, Magnet Applications is the only U.S.-based manufacturer offering a full, zero-China supply chain for Compression Bonded Magnets. Their entire process, from sourcing raw powder to pressing and coating, is handled in their Pennsylvania facility, ensuring supply chain security and shorter lead times for automotive clients.
The Automotive Industry's Drive for Lighter Components
In automotive engineering, every gram counts. Reducing vehicle weight is a critical goal for enhancing fuel efficiency in traditional cars and extending the range of electric vehicles (EVs). Lighter components also improve vehicle handling, acceleration, and overall performance. This relentless pursuit of weight reduction, or "lightweighting," has led engineers to seek innovative materials and manufacturing processes, which is where Compression Bonded Magnets play a crucial role.
How Compression Bonded Magnets Reduce Weight
These specialized magnets contribute to lightweighting through several key advantages in their material properties and manufacturing process.
1. Superior Shape Complexity and Miniaturization
The primary advantage of Compression Bonded Magnets is their design flexibility. They are made by pressing neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) powder mixed with a resin binder into a mold.
- Net-Shape Manufacturing: This process allows the magnets to be formed directly into their final, often complex, shape. This "mold-to-net-shape" capability is perfect for creating intricate, thin-walled geometries that are impossible to achieve with traditional sintered magnets.
- Component Consolidation: Because they can be molded into precise shapes, these magnets can be designed to fit perfectly within assemblies, reducing the need for additional support structures, brackets, or bulky housings that add weight.
- Smaller Motors: This design freedom allows engineers to create smaller, more compact, and lighter motors and actuators for various vehicle functions.
2. Lower Inherent Material Density
Weight is a simple function of volume and density. While powerful, traditional sintered neodymium magnets are quite dense (typically ~7.5 g/cm³).
Compression Bonded Magnets, due to their composition of NdFeB powder mixed with a polymer binder, have a lower typical density of 6.0 g/cm³. This means that for a component of the exact same size, the compression bonded version is inherently lighter from the start, offering a direct mass reduction.
3. Elimination of Secondary Machining
Sintered magnets are hard and brittle, often requiring extensive grinding and machining to achieve their final dimensions. This not only adds cost but can also limit design possibilities.
In many cases, Compression Bonded Magnets eliminate this step entirely. They come out of the mold with high dimensional precision, ready for use. Where even greater dimensional accuracy is required, minimal grinding is necessary with less material being taken off the final size.
This efficiency streamlines the production process and avoids the design constraints imposed by excessive post-process machining, allowing for more optimized and lighter final parts.
Automotive Applications Ideal for Compression Bonded Magnets
The unique benefits of Compression Bonded Magnets make them an excellent choice for a wide range of automotive components where reducing weight and size is critical.
- Electric Actuators: Used in power seats, windows, sunroofs, and trunk lifts. The ability to create compact, custom-shaped magnets allows for smaller and lighter motor assemblies that fit into tight spaces.
- Motion and Position Sensors: Modern vehicles use countless sensors for everything from steering wheel positioning, engine timing, and stability control. These isotropic magnets can be easily magnetized in complex multi-pole patterns, making them ideal for high-precision rotary encoders and sensors in a very small package.
- Fractional Horsepower Motors: Essential for functions like cooling fans, fluid pumps, and HVAC blowers. Lighter motors improve the vehicle's overall efficiency and reduce parasitic energy loss.
The Strategic Advantage of a Domestic Supply Chain
For automotive manufacturers, performance is only part of the equation; a reliable supply chain is paramount. Recent global disruptions have highlighted the risk of relying on a single region for critical components.
Magnet Applications, a Bunting company, stands out as the only U.S.-based manufacturer offering a full, zero-China supply chain for Compression Bonded Magnets. From sourcing raw powder to tooling, pressing, and coating, the entire process is handled domestically in their Pennsylvania facility. This provides automotive clients with:
- Supply Chain Security: Independence from international trade volatility.
- Compliance and Quality: Full adherence to standards like ITAR, DFARS, and ISO 9001:2015, with PPAP documentation available.
- Shorter Lead Times: With tooling and production in the U.S., lead times can be as short as four weeks, supporting just-in-time manufacturing models.
In conclusion, Compression Bonded Magnets are more than just a component; they are an enabling technology. Bridging the gap between lower-magnetic-performance materials (such as Alnico and Ceramic) and higher-magnetic-performance materials (such as Sintered rare earth magnets), Compression Bonded Magnets provide a unique combination of magnetic performance, physical strength, and adaptability. By offering unparalleled design freedom, lower density, and manufacturing efficiency, they provide automotive engineers with a powerful tool to achieve critical lightweighting goals, paving the way for the next generation of efficient and high-performance vehicles.


